Abstract
The concept of implementing National Strategy for Financial Education has been gradually building. Most of the nations globally take initiative for implementing sound National Strategy for Financial Education. Whereas some developed countries already have their unified and coordinated national strategy for financial education. India is having second largest population in the world. There is an urgent need to develop a sound and stable financial system. it is more necessary to quickly formulate and implement a national strategy. Financial Literacy and Financial Education play important role in financial inclusion, inclusive growth and sustainable prosperity. Financial Literacy develops confidence, knowledge and skills to manage financial products and services enabling them to have more control of their present & future circumstqnces.59 countries worldwide are implementing National Strategy using guidance from the OECD/INFE high level principles on National Strategy for Financial Education. Several empirical studies have found that financial literacy level amongst Indians low by global standards. The need of the hour is to boost up financial education initiatives and comprehensive research should be done on national strategy for financial education. The present study aims at finding the role and relevance of financial education in India.
1.Introduction
According to OECD Financial Education is a combination of financial awareness, skills, attitude and behaviour essential to make better financial decision in order to achieve individual financial wellbeing. Any individual can achieve financial literacy through the process of financial education. When it comes to creating an efficient economy, financial stability and financial literacy are the two sides of the same coin. In this context the Government of India and Reserve Bank of India have begun to include both financial literacy and financial education in their devel-opment agenda. On 20 August2020, the RBI released revised National Strategy for Financial Education (NSFE) for 2020-2025,the second one after the 2013-18 (NSFE) RBI released 5-core strategy that is content, capacity, community, communication, and collaboration for promoting financial education in country strategic include skilling on financial education, encouraging savings behaviour, developing credit discipline, improved usage of digital financial services and creating awareness on avenues for grievance redressal. Financial literacy rate in India has consistently decline compared to other nations of the world. According to a 2014 global survey by Standard & Poor’s nearly76% young population in India does not understand even the basic financial concepts. According to the India Spend report 75% of the country’s population does not have any form of life insurance and only 8% Indians protect their family from financial shock in case of the death of an earning member. Financial illiteracy creates a burden on the nation as it needs to spend more on creating financial security for citizens.
2. Literature Review
Financial literacy and Education influence individual to understand the finance concepts and they able to take rational financial decision (Huston 2010). As per the OECD, the designed framework of National Strategy for Financial Education promotes a smooth and sustainable co-operation between finance regulators and stakeholders, to avoid duplication of resources and allows development of articulated and tailored way with measurable and realistic objectives depend on dedicated national assessments. Some Nations like Australia, Spain, United Kingdom, Czech Republic, Netherlands and New Zealand have already implemented policy to set up a National Strategy for Financial Education. Where as many other nations are in the stage of forming and implementing a government policy for setting up a unified and coordinated National Strategy for Financial Education in these countries. The OECD International Network on Financial Education pilot study conducted by Atkinson and Messy (2012) on financial literacy in 14 countries focusing particularly on levels of financial knowledge, financial behaviours and attitudes. The study highlight that there is a lacking of financial awareness, knowledge skills among a sizeable proportion of the population in each of the countries surveyed and it appears that the level of financial awareness in women is less than man from the countries surveyed. Hung et.al.(2012) undertook a review of existing literature on gender differences around the world regarding financial literacy and find that women’s knowledge about financial concepts is less than the men they not able to take sound financial decision. The above studies clearly states that the impact of financial education for an individual and also for financial growth of a country.
3. Methodology
The design of research study is exploratory. The data used is secondary which is from journals, research papers, newspapers. Some websites are also used to studied and for collecting the required data.
4. Importance of Financial Education in India
Today, India is one of the biggest markets for the business enterprises. Its large number of population is seen as an asset by the various Multinational companies. There has been a steady increase in foreign investments and many Indian companies have expanded their business operations to globally. Now India is emerging as one of the fastest-growing economic country in the world. However, many small producers, companies and Indian firms aren’t able to succeed. We have developed ourselves in technology and to some extent in production field, but most of us fail because of financial mismanagement. According to the census conducted in 2011 large portion of popula-tion, i.e., 74.04% of the total population is not aware about the basic financial concepts, only a few can understand the basic fundamentals of finance. According to the report conducted by the Global Financial Literacy Excellence Centre (GFLEC), only 24% of the Indians of adult population is financially literate. In comparison to other emerging economies, the financial literacy rate of India is the lowest. Whereas other emerging economies have better financial literacy rates, there’s still scope for more improvement (Fig 1 and 2).
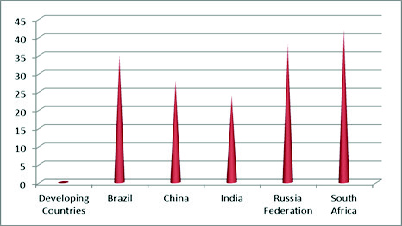
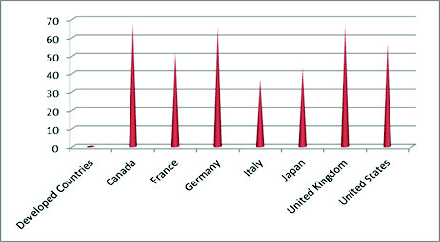
As we compare the literacy rate of different states we observe that state like Gujarat, Goa and Kerala have financial literacy rates 83%, 50%and 36% respectively which show that there general literacy rate also comparatively with other state is high (Table 1).
Table 1: State wise level of Financial Literacy in India (2015)
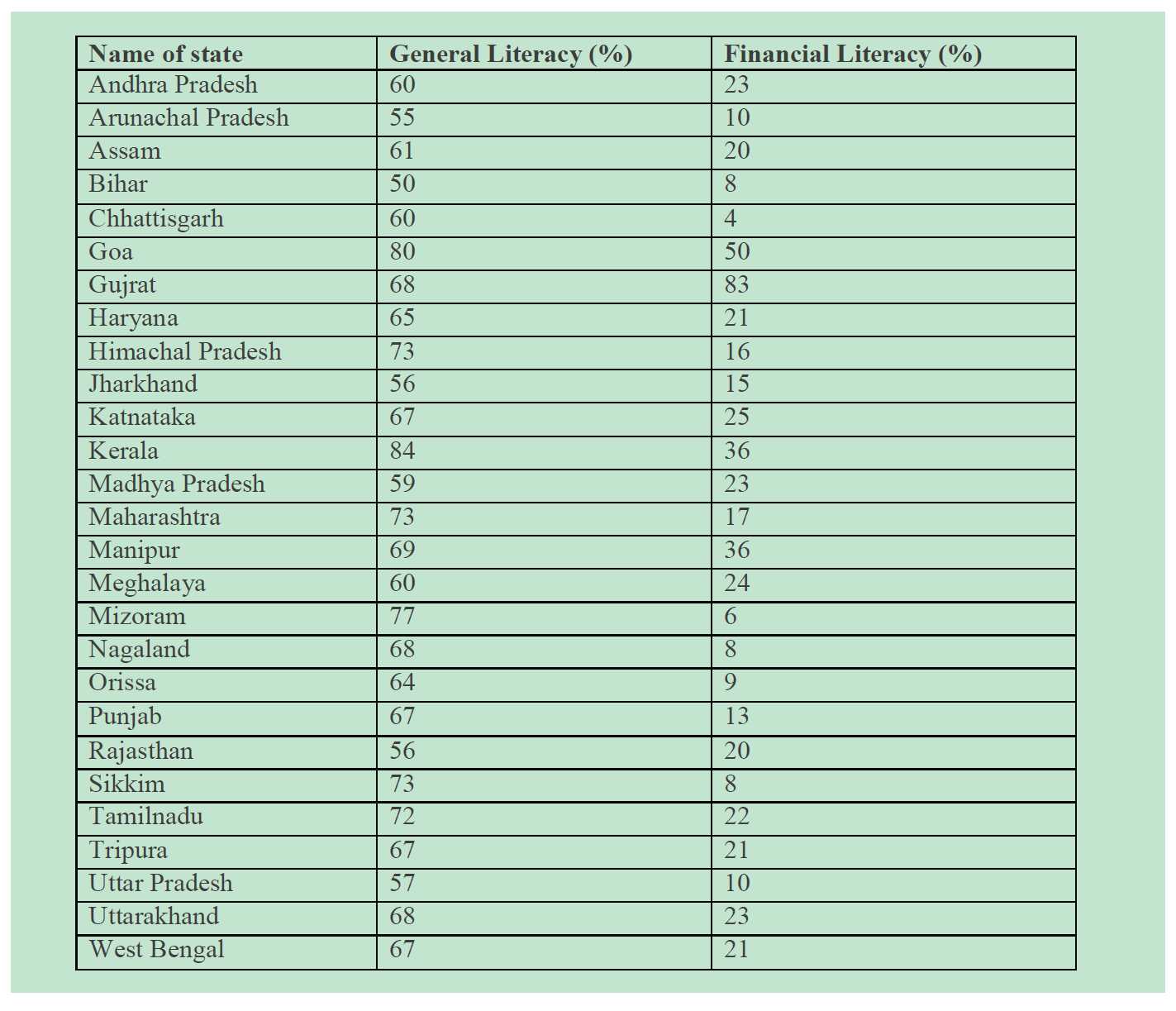
That means education influence the rate of financial literacy. Whereas state like Maharashtra, Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh have financial literacy rate 17%, 20% and10% respectively show low financial literacy rate because of this the general literacy rate also low.
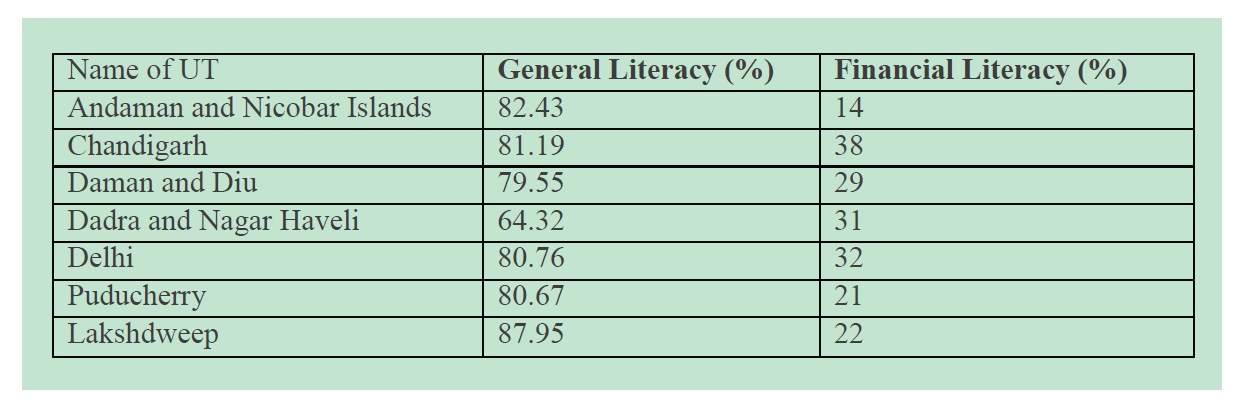
Union-Territories wise levels of Financial Literacy in India is presented in Table 2 which showed highest general literacy in Lakshdweep (87.95 %) and highest financial literacy in Chandigarh (38 %). There is an urgent need for the government to set up national strategy for financial education that improve financial literacy of a nation.
Table 2: Union territories wise Level of Finance Literacy in 2015
5. Efforts made so far by the regulating authority in the field of Financial Education
RBI’s initiatives on Financial Education:
Reserve Bank of India has undertaken the various project to disseminate information regarding the general banking aspects to various target groups, including school students, college students, women, senior citizen, defence personnel through the project titled i.e., “Project Financial Literacy”. There vision is to disseminated to the target audience with the help of banks, local authorities, schools and colleges through presentations, pamphlets, brochures, seminars, films and also through their websites. The initiates which are undertaken by the RBI’s at their initial stage which results can be seen in coming years.
SEBI’s Initiatives on Financial Education:
Securities Exchange Board of India organised a nationwide campaign for the wide spread of financial education to empower the nation. SEBI undertake financial education to various target segment i.e., school students, college students employers, employees as well. Some education programmes also conducted by the SEBI to imparting financial awareness among the investors . SEBI also publishes study material in English and other regional languages. SEBI efforts to uplifting the financial education help the nation for making a healthy environment for prospectiveinvestor.
6. Concluding Remark
Given the emphasis on education in India, it should be possible to enhance the financial literacy among Indians. The financial education can be improved through inclusion of relevant material on financial literacy in the general education program of schools and colleges. The initiative by the government for improv-ing financial education for well-being of individuals in India should be focusing the young investors. In India, various regulating authority such as RBI, SEBI, IRDA, PFRDA are doing a commendable job to attain the goal of financial literacy and education. At present there are very few studies so far conducted in the area of financial literacy and education of the nation. Today’s need is to strengthen financial education initiatives in India and comprehensive research should be done on National Strategy for Financial Education in India.
References
- Atkinson A and Messy F. (2012). Measuring financial literacy. Results of the OECD/International Network on Financial Education (INFE) Pilot Study. In OECD Working Papers on Finance. Insurance and Private Pensions; No. 15; OECD Publishing: Paris,-France,https://rbidocs.rbi.org.in/rdocs/-PublicationRe-port/Pdfs/NSFE016072012.pdf
- Hung A, J Yoong and E Brown (2012). “Empowering Women Through Financial Awareness and Education”, OECD Working Papers on Finance, Insurance and Private Pensions, No. 14, OECD Publishing. http://dx.doi.org/10.1787/5k9d5v6kh56g-en https://street-fins.com/the-importance-of-financial-lit-eracy-in-india Huston S (2010). Measuring financial literacy. J. Consum. A. 44, 296–316.
- OECD/INFE. (2011) Measuring financial literacy. In Core Questionnaire in Mea-suring Financial Literacy: Questionnaire and Guidance Notes for Conducting an Internationally Comparable Survey of Financial Literacy; OECD: Paris, France.
- OECD (2013) Improving Financial Education Effectiveness through Behavioural Economics-OECD Key Findings and Way Foreward; OECD: Paris, France.
DOI
https://doi.org/10.57259/GRJ7773
Research Objectives
Understand the need of financial education.Importance of Regulatory Authorities towards uplift the financial education in India.
Research Objectives
- To understand the need of financial education.
- Importance of Regulatory Authorities towards uplift the financial education in India.
- What is the relevance of National Strategy for financial education in nation building.
Bio

Dr. Asha Rani is a person of versatile expertise. Dr. Asha Rani is currently working as Inde-pendence researcher. She is a highly interac-tive trainer and Consultant whose work is mainly based on research work.



